What is a branch pipe used for?
2024-09-12
A branch pipe is a piping component used to create a connection between a main pipeline and one or more subsidiary pipelines. It allows fluid (liquid, gas, or steam) to flow from the main line into smaller branch lines, which may serve different areas or systems.
Key Uses of a Branch Pipe:
1. Diverting Flow:
- It enables the distribution of flow from a larger pipeline to smaller, localized systems or equipment.
2. Connecting Different Systems:
- A branch pipe connects the main pipeline to subsidiary systems such as tanks, pumps, or other machinery in industrial settings.
3. Regulating and Controlling Flow:
- By controlling the flow into separate branches, it helps regulate the flow rate or pressure in different parts of a piping network.
4. Utility Distribution:
- In buildings, branch pipes are often used for distributing utilities like water, gas, or air from a central supply line to various rooms or locations.
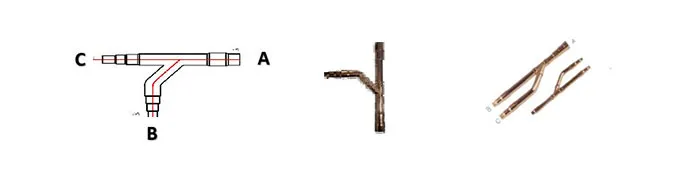
Common Applications:
- Plumbing: Used to connect water lines in homes or buildings to sinks, showers, or toilets.
- Industrial Systems: Applied in chemical plants, refineries, or power plants to distribute process fluids.
- Firefighting Systems: Branch pipes help direct water from a main line to hoses or sprinkler systems.
In summary, branch pipes are essential in creating a network of connections within a piping system, ensuring the efficient flow and distribution of fluids or gases to various parts of a system or structure.


